Why Enterprises Need Zero Trust Security in Backup Solutions

In today’s digital-first environment, where data breaches are not just mishaps, embracing zero trust is essential. These inevitabilities highlight the importance of robust, reliable backup solutions for enterprises. However, simply having a backup system is no longer enough. Cyberthreats evolve and consequently the approach to securing backup architectures must also evolve.
Zero-trust data security offers a promising enhancement to traditional methods. We must prioritize stringent access controls. Continuous validation is essential.
According to the survey conducted by Entrust, 57% of respondents have or will implement Zero Trust in their encryption plans or strategies, underscoring its vital importance in organizational security. Additionally, 18% of organizations have already implemented all Zero Trust principles, 14% have established a foundation for a Zero Trust strategy, and 17% are currently exploring various solutions to aid in its implementation.
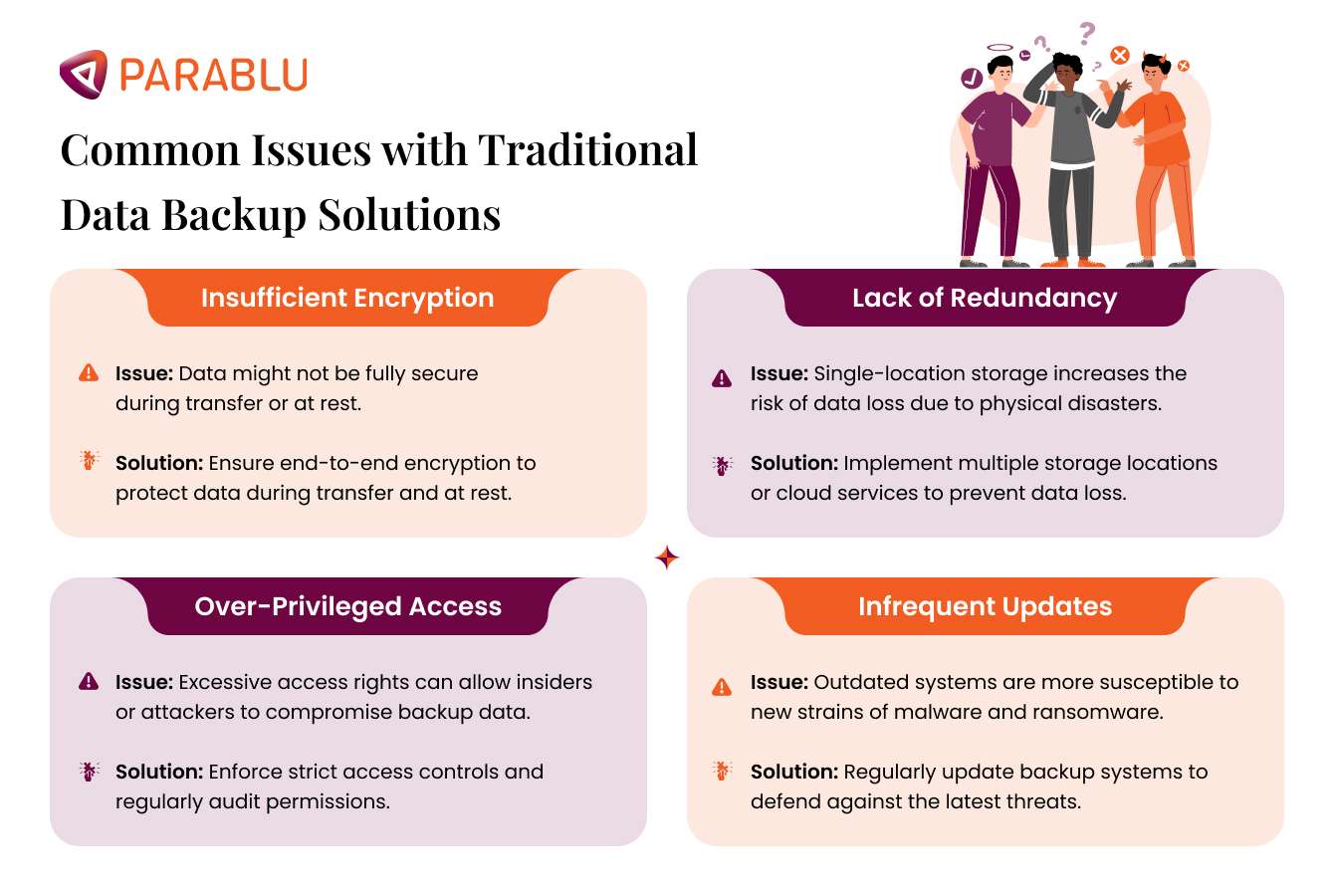
An overview of vulnerabilities in traditional backup solutions
Traditional backup solutions, while foundational, are fraught with vulnerabilities. Without a zero-trust model in cyber security, these systems can be the weak links in your data security strategy.
Common issues include:
- Insufficient encryption: Data might not be fully secure during transfer or at rest.
- Lack of redundancy: Single-location storage increases the risk of data loss due to physical disasters.
- Over-privileged access: Excessive access rights can allow insiders or attackers to compromise backup data.
- Infrequent updates: Outdated systems are more susceptible to new strains of malware and ransomware.
Let’s understand zero trust in a simpler way through an analogy.
Imagine a large apartment complex with hundreds of residents. Traditionally, security might work like this:
- One Key Fits All: Everyone has a single key that unlocks the main entrance and all individual apartments. This is like a traditional network security model where everyone with a valid login can access everything.
- Limited Verification: Security guards at the main entrance might only check for a valid key and not verify the resident’s identity. This reflects a system that relies solely on usernames and passwords for authorization.
However, zero trust security is like a more sophisticated system:
- Multi-Factor Authentication: To enter the building, residents need a key fob and a unique code sent to their phone. This represents additional verification beyond just a login credential.
- Zoned Access: Residents can only access their own floor and apartment, not others. This translates to users only having access to the specific data and resources they need for their job functions.
- Continuous Monitoring: Security cameras and activity logs track all movement within the building. Similarly, a zero-trust system constantly monitors user activity and identifies suspicious behavior.
Combat emerging threats with zero-trust security
The cyber-threat environment has never remained static. What was considered secure yesterday might be vulnerable today. In this regard, enterprises must monitor emerging threats and consistently maintain their competitive edge with best data backup methods.
Updating backups frequently, reviewing access rights with zero trust, and deploying the latest security technology are ways of guaranteeing resilience in the face of current risks.
Introduction to the concept of zero trust in cybersecurity
Zero trust is a security framework. It operates on the principle “never trust, always verify.” It advocates for rigorous identity verification. There are strict access controls. Verify everyone. It assumes threats can exist both outside and inside traditional network boundaries. Therefore, authenticating every individual and device is necessary. Access to network resources requires authorization. Unlike conventional security models that enforce perimeter-based defenses, Zero Trust requires continual verification of all entities.
Constant verification is essential in today’s security framework. This approach has become increasingly relevant as enterprises shift towards cloud-based services. Zero trust principles prevent the exploitation of compromised credentials or lateral movements within the environment. Implementing zero trust in backup solutions significantly enhances security. It addresses many vulnerabilities inherent in traditional systems. These are just a few of the many benefits of zero trust security.
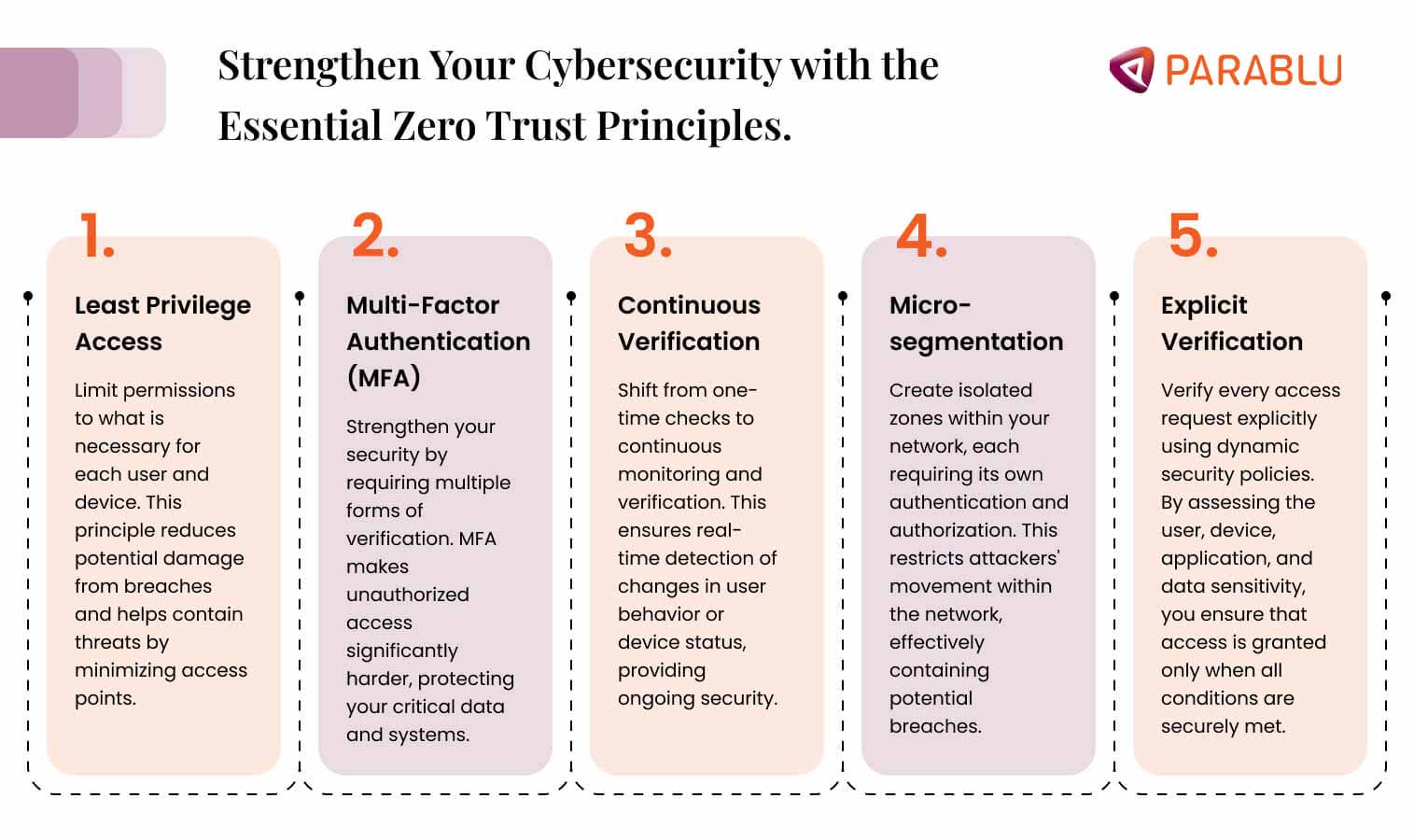
Principles of the Zero Trust Model
It is essential for businesses to have trusted security measures. Generally, the zero trust model is based on strict verification processes, least privilege access controls, divisions into segments, and a pro-action security posture. Taken together, these principles help create a secure digital space that can effectively resist contemporary dynamic threats and attacks.
Key principles that underscore this approach:
- Least Privilege Access: Each user or device gets only the minimum access needed for their tasks. This limits damage if a breach occurs, since attackers can’t access much from a single compromised account or device.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA requires users to provide multiple proofs of identity, greatly reducing unauthorized access.
- Continuous Verification: Instead of a one-time check, Zero Trust constantly monitors and verifies the security of users and devices throughout their session.
- Micro-segmentation: Resources are divided into secure zones, and users need to be authenticated and authorized to access each zone. This reduces attackers’ ability to move within networks.
- Explicit Verification: Every access request must be verified using dynamic security policies that consider the user, device, application, and data sensitivity.
Organizations must incorporate zero trust into their backup solutions to ensure the security and integrality of their data backups. As a result, adopting a zero trust approach to data security will help to protect data throughout its lifecycle, significantly reducing cyber risks. By rigorously applying these zero-trust principles, businesses can enhance their security posture against a changing threat environment.
Zero Trust Use Cases
Zero Trust operates on the premise that threats can exist inside and outside the network. Therefore, the network constantly verifies every request, whether from the inside or outside, as if it originates from an open network. This approach is particularly relevant in scenarios like:
- Remote access to data: Ensures secure access for remote workers by constantly verifying every request.
- BYOD (Bring Your Own Device): Protects enterprise data on personal devices through continuous authentication and authorization.
- Insider threats: Mitigate risks by not trusting any user or device by default, even those within the network.
- Network segmentation: Limits lateral movement of attackers by dividing resources into secure zones and requiring authentication for each zone.
Benefits of Zero Trust Security in Backup Solutions
Incorporating zero trust features into backup solutions enhances an enterprise’s ability to protect data against ransomware or a growing array of cyber threats. Implementing zero trust measures can transform how backup solutions are perceived. Below are a few of the benefits of zero trust security:
- Data encryption and authentication
Zero Trust principles-based backup solutions encrypt data both in transit and at rest, thereby reducing the risk of data breaches. Furthermore, robust authentication mechanisms strictly control data access, granting it only after rigorous verification. This not only helps to protect sensitive information, but it also complies with regulatory data protection requirements.
- Access control and authorization
Access controls are a fundamental aspect of any Zero Trust architecture. Backup solutions can provide dynamic and adaptive protection by granting access rights to users and devices based on their identity, context, and real-time assessment of their risk and trust levels. This includes mechanisms for minimizing user privileges and employing just-in-time and just-enough-access (JITA/JEA) policies to further reduce the attack surface.
- Threat detection and response mechanisms
Zero Trust backup solutions not only prevent unauthorized access but continuously monitor for anomalous behavior, automatically adjusting controls and responding to potential threats in real time. These systems integrate advanced analytics and automated responses to detect and mitigate threats before they can cause significant harm. Enterprises can significantly reduce response times and mitigate the damage from cyber incidents, thereby ensuring business continuity and resilience against attacks.
Integration of Zero Trust Features in Enterprise Backup Solutions
Incorporating zero trust features into enterprise backup solutions fundamentally reinforces data protection. This integration ensures that backup data is protected equally against threats, just like operational data. Standardize secure authentication, role-based access control, encrypted data storage and transfer to align backup processes with Zero Trust principles.
- Implementation challenges and considerations
Implementing zero trust features within an enterprise backup environment presents several challenges. Firstly, the complexity of existing IT environments can make uniform policy enforcement difficult. Organizations may struggle with legacy systems that are not compatible with newer, zero trust policies. Furthermore, the initial setup requires careful planning and potentially significant adjustments to infrastructure and operational procedures. Training for IT staff and users is crucial, as they need to understand and properly follow the new security protocols to ensure their effectiveness.
- Zero Trust vs. other technologies like software-defined perimeter (SDO), VPN, etc.
Zero Trust security demands rigorous identity verification for every entity trying to access resources on a network, which sets it distinctly apart from other technologies.
In contrast to a VPN (virtual private network) that allows access to an entire network once connected, zero trust only gives access to necessary resources, thereby minimizing possible security breaches.
Unlike the Software-Defined Perimeter (SDP), which creates virtual boundaries to protect assets, zero trust requires continuous validation of security credentials regardless of the user’s location or device, offering real-time defense adjustments.
Zero knowledge proof, another technology, ensures that one party can prove to another that a given statement is true, without conveying any additional information apart from the fact that the statement is true. This aligns with zero trust’s requirement for the minimum necessary data exposure. However, zero trust integrates continuous monitoring and validation to adapt to changes in threats or anomalies, making it a more dynamic approach.
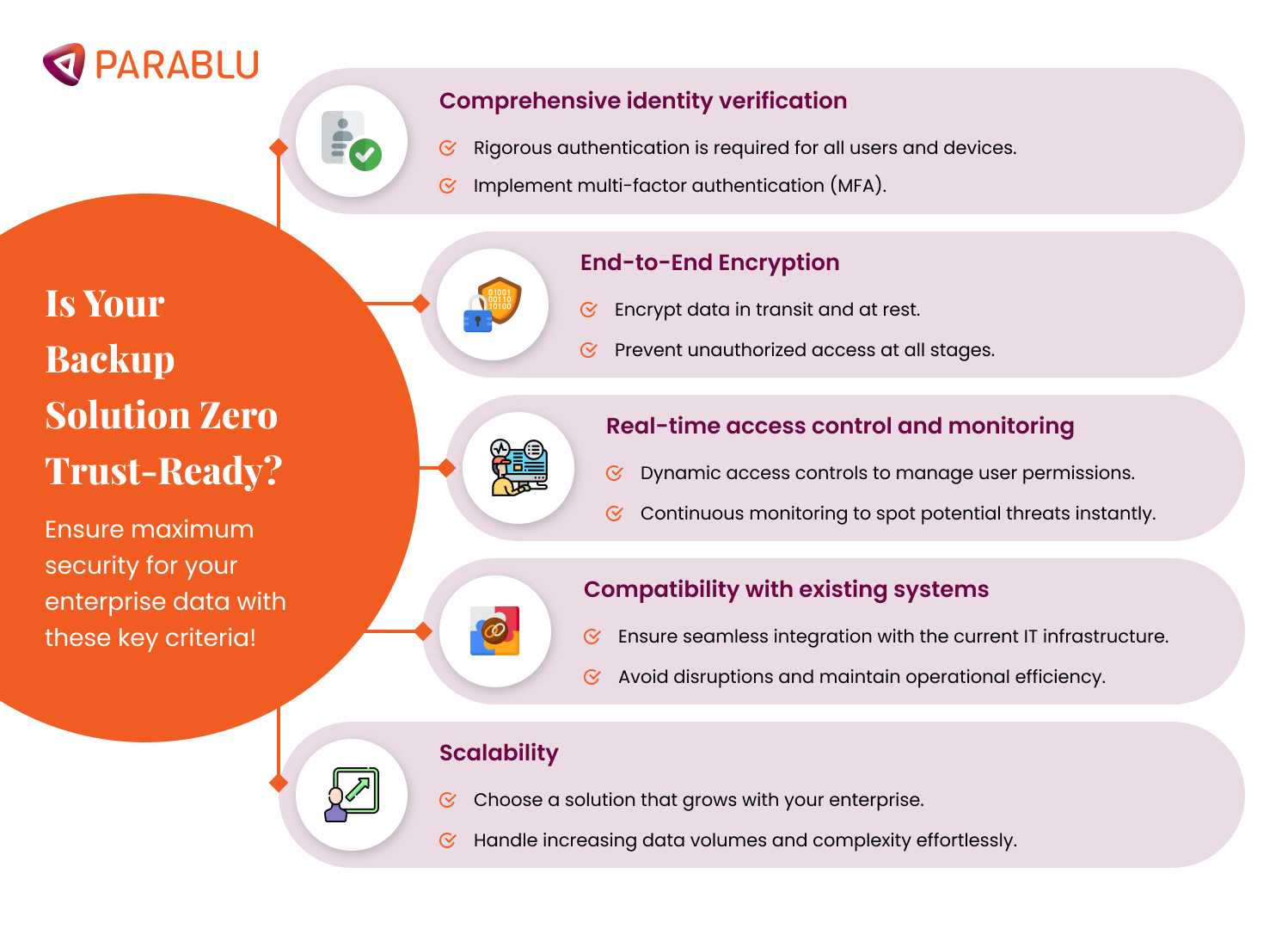
Recommendations for enterprises seeking zero trust backup solutions
When evaluating backup solutions that incorporate zero trust principles, enterprises should consider the following key criteria:
- Comprehensive identity verification: Ensure the solution includes rigorous authentication mechanisms for all users and devices.
- End-to-end encryption: It’s important to encrypt data both in transit and at rest to prevent unauthorized access.
- Real-time access control and monitoring: The ability to dynamically control access and monitor data access patterns can help identify potential security threats immediately.
- Compatibility with existing systems: Integration with your current IT infrastructure is critical to implementing a seamless and effective Zero Trust policy.
- Scalability: As enterprises grow, the backup solution should be capable of scaling to handle increased data and more complex operations.
Selecting a zero trust-enabled backup solution empowers enterprises to prevent data breaches by ensuring that each access request is strictly verified and monitored, significantly enhancing overall data security.
Parablu’s Zero Trust Commitment for Robust Data Security
From the start, our focus has always been on safeguarding your data at Parablu. We’ve set up a zero trust system, which means we don’t just trust anyone or any device automatically, regardless of their origin. Every time someone requests access, they must go through processes involving factor authentication and strict authorization. Only those who possess the necessary credentials and permissions can gain entry.
That’s not all. We are taking steps to fortify our network. Through micro-segmentation, we separate segments of the network so that even if someone gains access, they can’t freely navigate and create chaos. We constantly monitor for any signs of trouble in real time. Additionally, we encrypt all your data during transmission. While it resides on our servers. This ensures that even if someone intercepts it, they won’t be able to decipher it without the decryption key.
Let’s not overlook our endpoint security protocols. We meticulously ensure that all your devices adhere to security criteria by conducting audits and assessments. Our commitment to safeguarding your data is unwavering. We remain vigilant about adapting to emerging cyber threats.
In essence, “We’re fully committed to ensuring the security and privacy of data.”
Conclusion
In today’s digital world, where everything is interconnected, it’s not just a good idea, but necessary to incorporate zero trust features into enterprise backup solutions. By adopting a zero-trust architecture, organizations can significantly enhance their data security, making it extremely difficult for cyber threats to break through their defenses.
And here’s the kicker: as the digital landscape keeps evolving and cyber threats become more sophisticated. Having strong backup solutions with zero trust principles is no longer optional; it’s a must-have.
Companies that implement these measures not only protect the integrity of their data, but also pave the way for a future that’s more resilient and secure. So, demanding zero trust features in backup solutions is a critical step for any company looking to shield themselves from the ever-increasing wave of cyberattacks.




